What is FASD?
Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder, FASD, is an umbrella term covering a range of disorders and malformations resulting from prenatal exposure to alcohol, including organ malformations, brain damage and developmental, cognitive and behavioral disorders.
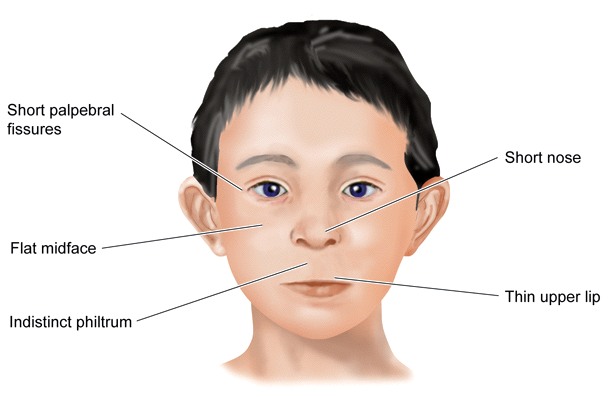
FASD encompasses the disorders fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS), partial fetal alcohol syndrome (pFAS) and alcohol related neurodevelopmental disorders (ARND). All subtypes of FASD are characterized with functional and/or structural abnormalities of the central nervous system. Children with FAS and pFAS also show facial anomalies and children with FAS are marked with growth deficits. All persons with FASD have lifelong cognitive, social and behavioral disabilities.
Examples of facial abnormalities common in FAS and pFAS. Note that flat midface and short nose are not diagnostic criteria for FAS.
No amount of alcohol is safe during pregnancy
Alcohol reduces fertility, increases the risk of miscarriage and preterm birth, and causes brain damage and birth defects of the child [1]. Prenatal exposure to alcohol can cause mental retardation, speech and motor disorders, deficits in visual-spatial skills, maths problems, deficits in memory and learning skills and executive function disorders as well as behavioral disorders and attention deficits. Difficulty with planning, anticipating consequences, understanding social situations and independently fulfilling everyday tasks significantly contributes to a very challenging life for persons with FASD and their environment. The complex impairments of persons with FASD often lead to a need for support for living and working. The prognosis might include unemployment, psychiatric illness, and criminality as negative outcomes [2].
Even moderate drinking or a single binge drinking episode can cause permanent damage [3 4 5]. The severity of FASD depends on factors such as the level of exposure, the developmental stage of the fetus [6] and nutritional status of the mother [7].
Prevalence of FASD
The prevalence of FASD has not been studied in all areas of the world. Diagnosis requires special medical expertise, so many cases are missed or misdiagnosed [8]. In the US, the prevalence of FASD is estimated at 1% [9], in Italy at 2 to 4% [10], and even higher in South Africa [11] and Russia [12]. FASD is the most common inborn chronic disease.
Prenatal exposure to alcohol is a cause of social inequality
Children with FASD are more likely to grow up in foster care, and youth with FASD are 19 times more likely to be incarcerated than youth without FASD [13]. IIn a population exposed to alcohol in utero, educational achievement was lower, while broken relationships and unemployment were higher [5]. Prenatal exposure to alcohol has thus been termed a “poverty trap” [14].
Prevention
There is no cure for FASD, but it can be prevented. The incidence of FASD can be reduced by public information campaigns, support of pregnant women, and clear preconception advice [15].
In addition to prevention, an improvement of care for people with FASD is urgently needed in order to enable them to have a satisfying participation in social life.
Reference List
1. Health Council of the Netherlands. Risks of alcohol consumption related to conception, pregnancy and breastfeeding. The Hague: Health Council of the Netherlands, 2005; publication no. 2004/22. ISBN 90-5549-000-8 [Summary in EN] [Full text in NL]
2. Streissguth, AP et al. Risk factors for adverse life outcomes in fetal alcohol syndrome and fetal alcohol effects. J. Dev. Behav. Pediatr. 25, 228-238 (2004). [Full text]
3. Willford, JA et al. Verbal and visuospatial learning and memory function in children with moderate prenatal alcohol exposure. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 28, 497-507 (2004). [Full text]
4. Barr, HM et al. Binge drinking during pregnancy as a predictor of psychiatric disorders on the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV in young adult offspring. Am. J. Psychiatry 163, 1061-1065 (2006). [Full text]
5. Nilsson, JP. Does a pint a day affect your child's pay? The effect of prenatal alcohol exposure on adult outcomes. Working paper 2008:4. 2008. Uppsala, IFAU--Institute for Labor Market Policy Evaluation. [Full text]
6. Ramsay, M. Genetic and epigenetic insights into fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Genome Medicine 2:27 (2010). [Full text]
7. Keen, CL et al. The plausibility of maternal nutritional status being a contributing factor to the risk for fetal alcohol spectrum disorders: the potential influence of zinc status as an example. Biofactors 36(2):125-35 (2010). [Full text]
8. Vagnarelli, F et al. A survey of Italian and Spanish neonatologists and paediatricians regarding awareness of the diagnosis of FAS and FASD and maternal ethanol use during pregnancy. BMC Pediatr. 2011 Jun 6;11:51. doi: 10.1186/1471-2431-11-51 [Full text]
9. Sampson, PD et al. Incidence of fetal alcohol syndrome and prevalence of alcohol-related neurodevelopmental disorder. Teratology 56, 317-326 (1997). [Full text]
10. May, PA et al. Epidemiology of FASD in a province in Italy: Prevalence and characteristics of children in a random sample of schools. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 30, 1562-1575 (2006). [PubMed record]
11. Olivier, L et al. Burden of fetal alcohol syndrome in a rural West Coast area of South Africa. S Afr Med J. 103, 402-5 (2013). [Full text]
12. Popova, S et al. What research is being done on prenatal alcohol exposure and fetal alcohol spectrum disorders in the Russian research community? Alcohol Alcohol. 49, 84-95 (2014). [Full text]
13. Popova, S et al. Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder prevalence estimates in correctional systems: a systematic literature review. Can J Public Health. 2011 Sep-Oct;102(5):336-40. [Full text]
14. Thanh, NX et al. Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder--poverty trap? J Popul Ther Clin Pharmacol. 20(1):e63-6. (2013). [Full text]
15. Kancherla, V. et al. Urgent global opportunities to prevent birth defects. Sem Fetal Neonatal Med 19, 153-160 (2014). [PubMed record]